 | A gold miner breaking through permafrost in the Canadian Yukon uncovered an almost completely intact baby woolly mammoth. The find, officials say, is the best-preserved specimen in North America to date and only the second full calf ever found. The 55-inch calf lived about 30,000 years ago, and was entombed at about one month of age. Paleontologists were stunned at the detail in the find. |
Thursday, June 30, 2022
30,000 yo baby woolly mammoth in Yukon
Wednesday, June 29, 2022
Hagia Sophia’s priceless marble floors damaged
 | Tiles of the ancient marble floors in Hagia Sophia have been damaged by heavy machines used to clean the site. The historic building was built as a church in the Byzantine era. It was previously a museum but was changed into a mosque in 2020. Work to effect this change is being blamed for the damage. |  |
 |  | The historic Imperial Gate in Hagia Sophia has also been badly damaged. The Imperial Gate, the central door of the building, is the largest and has been dated to the 6th century AD. |
Friday, June 24, 2022
Werewolf
 | Belief in werewolves developed in parallel to the belief in witches. Most modern fiction describes werewolves as vulnerable to silver and resistant to injury. These features appeared in German folklore of the 19th century. |
Wednesday, June 22, 2022
The Tyrant Collection
Monday, June 20, 2022
Sanxingdui relics
 | A sacrificial altar are among a treasure trove of 13,000 relics dating back over 3,000 years discovered by archaeologists in southwest China. The relics -- many made of gold, bronze and jade -- were unearthed in six sacrificial pits at the Sanxingdui archaeological site, near Chengdu. The Sanxingdui culture left behind no records. It is thought to be part of the ancient kingdom of Shu. It ruled in the western Sichuan basin along the upper stream of the Yangtze River until it was conquered in 316 BC. |
 Researchers described a turtleshell-shaped box made of bronze and jade as among their more intriguing finds. It is the first time such an object has been found. |   |
Thursday, June 16, 2022
Cambodia the ancient ‘Land of Gold’?
Wednesday, June 15, 2022
Roman bust fetches $930k
Tuesday, June 14, 2022
Amazing artifacts at Heritage
 | World War I Propaganda by James Montgomery Flagg (Leslie-Judge Co., 1917) D-Day: First American Flag Planted on Normandy Beachhead. |  |
Sunday, June 12, 2022
Assyrian Empire collapsed due to climate change
 | Ancient Mesopotamia, the land between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers, was the center of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. The ancient superpower was the largest empire of its time, lasting from 912 BC to 609 BC in what is now Iraq and Syria. At its height, the Assyrian state stretched from the Mediterranean and Egypt in the west to the Persian Gulf and western Iran in the east. Then a reversal of fortune, and the Neo-Assyrian Empire plummeted from its zenith (650 BC) to complete collapse within the span of a few decades. The reasons why were a mystery. Research shows that climate change was the double-edged sword that first helped the meteoric rise of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and then lead to its precipitous collapse. |
Friday, June 10, 2022
Treasures of Ancient Nubia
 Gilt-silver mummy mask of Queen Malakaye (664–653 BC) | An exhibition at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, titled 'Gold and the Gods: Jewels of Ancient Nubia', provided insight into the meticulous craftsmanship of Ancient Nubia. The show included more than 100 treasures from the MFA’s collection of jewelry from Ancient Nubia. The MFA’s collection dates from 1700 BC to AD 300 and is considered the most comprehensive of any outside of Khartoum. Gold and the Gods showcased elaborate necklaces, amulets, stacked bracelets, and earrings discovered inside the tombs of Nubian kings and queens. Ancient Nubia ruled the entire Nile Valley during the apex of its power in the eighth century BC. Nubian artisans turned out some of the most sophisticated, finely crafted jewelry of the ancient world. |  Hathor-headed crystal pendant (743–712 BC) Hathor-headed crystal pendant (743–712 BC) |
 | The exhibition included jewelry made with lapis lazuli, blue chalcedony, amethystine quartz, and carnelian. Some pieces incorporate enamel and glass, rare and valuable materials. Owners valued jewels as signs of wealth and status, but also for magical powers that protected them in life and the afterlife. |  |
 Nubian goldsmiths and jewelers employed methods that wouldn’t be reinvented in Europe for another thousand years. Nubian goldsmiths and jewelers employed methods that wouldn’t be reinvented in Europe for another thousand years. |  |  |
 |  |
Wednesday, June 8, 2022
Ancient Egyptian statue of Sekhemka
 | The statue is now believed to be in the U.S. The culture minister, Ed Vaizey, announced a four-month temporary export bar on the figure, which dates from c2400BC and is considered the finest example of its kind anywhere in the world and of “outstanding aesthetic importance”. The Sekhemka statue is a tomb model of a high official, wearing a short kilt and tight-fitting wig, surrounded by his wife, son and seven offering-bearers. He holds a papyrus on his knees on which are inscribed a list of offerings designed to serve the needs of the dead, including beer and cakes. |   |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)



















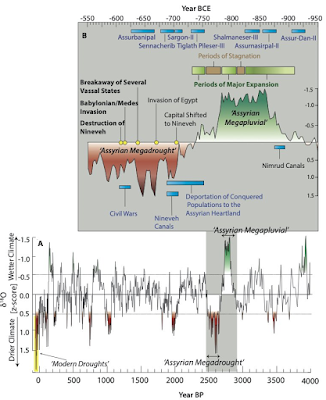
 Repeated crop failures likely exacerbated political unrest in Assyria, crippled its economy and empowered adjacent rivals.
Repeated crop failures likely exacerbated political unrest in Assyria, crippled its economy and empowered adjacent rivals.

